Project: astro-provider-databricks
Affordable Databricks Workflows in Apache Airflow
Project Details
- Latest version
- 0.1.5
- Home Page
- None
- PyPI Page
- https://pypi.org/project/astro-provider-databricks/
Project Popularity
- PageRank
- 0.005350478010630418
- Number of downloads
- 42499
Databricks Workflows in Airflow
The Astro Databricks Provider is an Apache Airflow provider to write Databricks Workflows using Airflow as the authoring interface. Running your Databricks notebooks as Databricks Workflows can result in a 75% cost reduction ($0.40/DBU for all-purpose compute, $0.07/DBU for Jobs compute).
While this is maintained by Astronomer, it's available to anyone using Airflow - you don't need to be an Astronomer customer to use it.
There are a few advantages to defining your Databricks Workflows in Airflow:
| via Databricks | via Airflow | |
|---|---|---|
| Authoring interface | Web-based via Databricks UI | Code via Airflow DAG |
| Workflow compute pricing | ✅ | ✅ |
| Notebook code in source control | ✅ | ✅ |
| Workflow structure in source control | ✅ | |
| Retry from beginning | ✅ | ✅ |
| Retry single task | ✅ | |
| Task groups within Workflows | ✅ | |
| Trigger workflows from other DAGs | ✅ | |
| Workflow-level parameters | ✅ |
Example
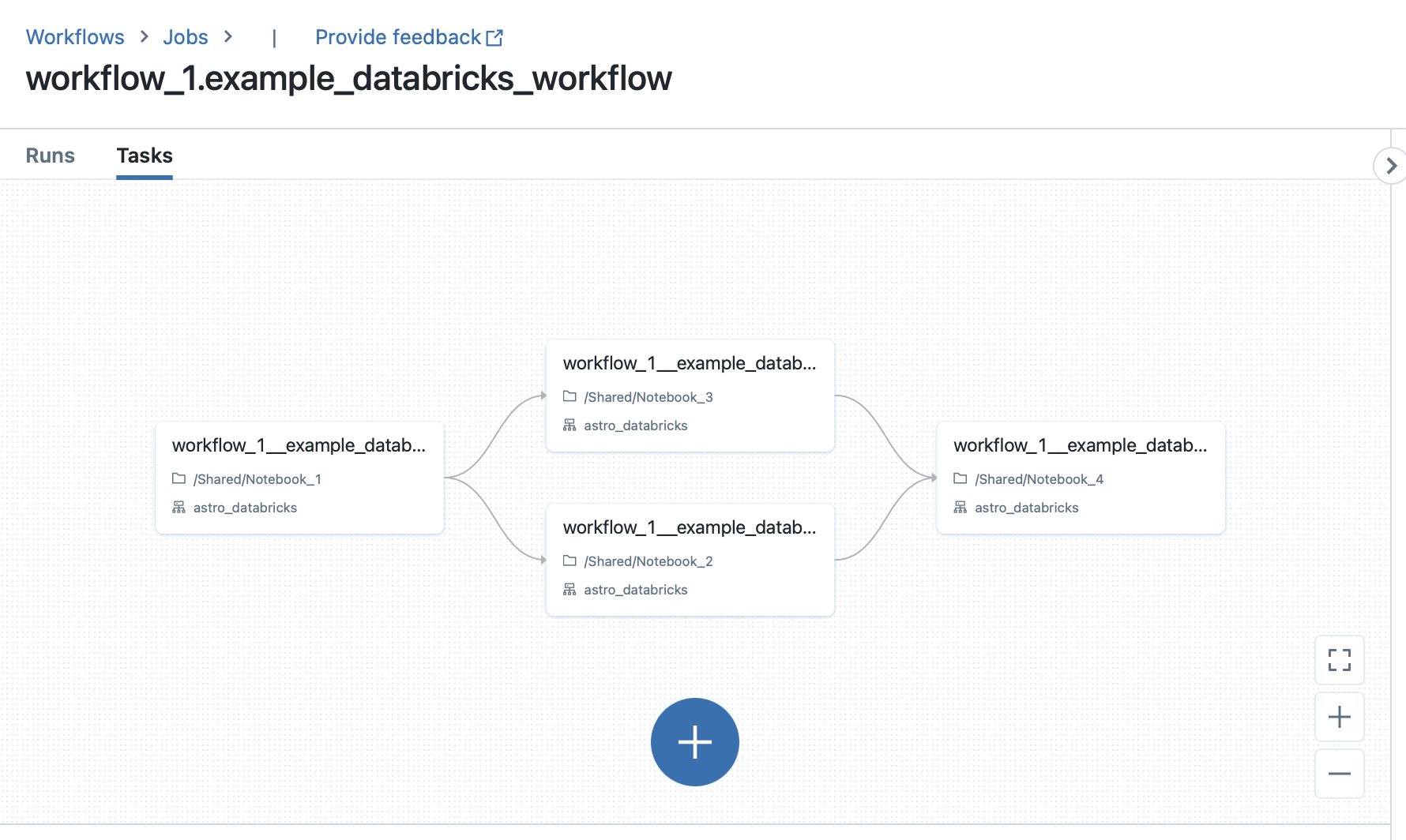
The following Airflow DAG illustrates how to use the DatabricksTaskGroup and DatabricksNotebookOperator to define a Databricks Workflow in Airflow:
from pendulum import datetime
from airflow.decorators import dag, task_group
from airflow.operators.trigger_dagrun import TriggerDagRunOperator
from astro_databricks import DatabricksNotebookOperator, DatabricksWorkflowTaskGroup
# define your cluster spec - can have from 1 to many clusters
job_cluster_spec = [
{
"job_cluster_key": "astro_databricks",
"new_cluster": {
"cluster_name": "",
# ...
},
}
]
@dag(start_date=datetime(2023, 1, 1), schedule_interval="@daily", catchup=False)
def databricks_workflow_example():
# the task group is a context manager that will create a Databricks Workflow
with DatabricksWorkflowTaskGroup(
group_id="example_databricks_workflow",
databricks_conn_id="databricks_default",
job_clusters=job_cluster_spec,
# you can specify common fields here that get shared to all notebooks
notebook_packages=[
{ "pypi": { "package": "pandas" } },
],
# notebook_params supports templating
notebook_params={
"start_time": "{{ ds }}",
}
) as workflow:
notebook_1 = DatabricksNotebookOperator(
task_id="notebook_1",
databricks_conn_id="databricks_default",
notebook_path="/Shared/notebook_1",
source="WORKSPACE",
# job_cluster_key corresponds to the job_cluster_key in the job_cluster_spec
job_cluster_key="astro_databricks",
# you can add to packages & params at the task level
notebook_packages=[
{ "pypi": { "package": "scikit-learn" } },
],
notebook_params={
"end_time": "{{ macros.ds_add(ds, 1) }}",
}
)
# you can embed task groups for easier dependency management
@task_group(group_id="inner_task_group")
def inner_task_group():
notebook_2 = DatabricksNotebookOperator(
task_id="notebook_2",
databricks_conn_id="databricks_default",
notebook_path="/Shared/notebook_2",
source="WORKSPACE",
job_cluster_key="astro_databricks",
)
notebook_3 = DatabricksNotebookOperator(
task_id="notebook_3",
databricks_conn_id="databricks_default",
notebook_path="/Shared/notebook_3",
source="WORKSPACE",
job_cluster_key="astro_databricks",
)
notebook_4 = DatabricksNotebookOperator(
task_id="notebook_4",
databricks_conn_id="databricks_default",
notebook_path="/Shared/notebook_4",
source="WORKSPACE",
job_cluster_key="astro_databricks",
)
notebook_1 >> inner_task_group() >> notebook_4
trigger_workflow_2 = TriggerDagRunOperator(
task_id="trigger_workflow_2",
trigger_dag_id="workflow_2",
execution_date="{{ next_execution_date }}",
)
workflow >> trigger_workflow_2
databricks_workflow_example_dag = databricks_workflow_example()
Airflow UI
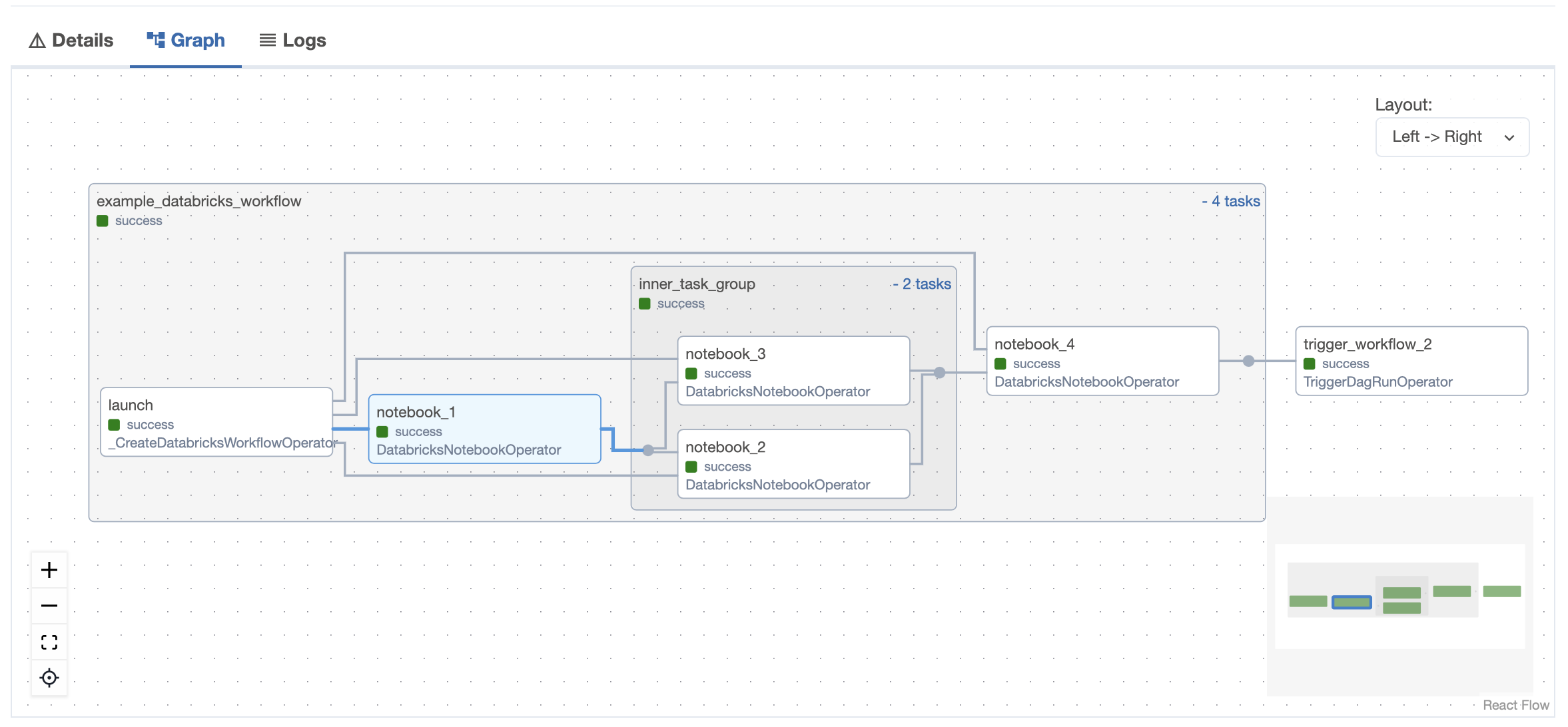
Databricks UI
Quickstart
Check out the following quickstart guides:
Documentation
The documentation is a work in progress--we aim to follow the Diátaxis system:
Changelog
Astro Databricks follows semantic versioning for releases. Read changelog to understand more about the changes introduced to each version.
Contribution guidelines
All contributions, bug reports, bug fixes, documentation improvements, enhancements, and ideas are welcome.
Read the Contribution Guidelines for a detailed overview on how to contribute.
Contributors and maintainers should abide by the Contributor Code of Conduct.