Project: pytorch-optimizer
optimizer & lr scheduler & objective function collections in PyTorch
Project Details
- Latest version
- 2.12.0
- Home Page
- https://github.com/kozistr/pytorch_optimizer
- PyPI Page
- https://pypi.org/project/pytorch-optimizer/
Project Popularity
- PageRank
- 0.0027854938718033066
- Number of downloads
- 37832
pytorch-optimizer
| Build | |
| Quality |   |
| Package |  |
| Status |   |
| License |  |
pytorch-optimizer is optimizer & lr scheduler collections in PyTorch.
I just re-implemented (speed & memory tweaks, plug-ins) the algorithm while based on the original paper. Also, It includes useful and practical optimization ideas.
Currently, 60 optimizers (+ bitsandbytes), 10 lr schedulers, and 13 loss functions are supported!
Highly inspired by pytorch-optimizer.
Getting Started
For more, see the documentation.
Most optimizers are under MIT or Apache 2.0 license, but a few optimizers like Fromage, Nero have CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 license, which is non-commercial.
So, please double-check the license before using it at your work.
Installation
$ pip3 install pytorch-optimizer
From pytorch-optimizer v2.12.0, you can install and import bitsandbytes optimizers.
please check the requirements before installing it.
$ pip install "pytorch-optimizer[bitsandbytes]"
Simple Usage
from pytorch_optimizer import AdamP
model = YourModel()
optimizer = AdamP(model.parameters())
# or you can use optimizer loader, simply passing a name of the optimizer.
from pytorch_optimizer import load_optimizer
optimizer = load_optimizer(optimizer='adamp')(model.parameters())
# if you install `bitsandbytes` optimizer, you can use `8-bit` optimizers from `pytorch-optimizer`.
from pytorch_optimizer import load_optimizer
opt = load_optimizer(optimizer='bnb_adamw8bit')
optimizer = opt(model.parameters())
Also, you can load the optimizer via torch.hub.
import torch
model = YourModel()
opt = torch.hub.load('kozistr/pytorch_optimizer', 'adamp')
optimizer = opt(model.parameters())
If you want to build the optimizer with parameters & configs, there's create_optimizer() API.
from pytorch_optimizer import create_optimizer
optimizer = create_optimizer(
model,
'adamp',
lr=1e-3,
weight_decay=1e-3,
use_gc=True,
use_lookahead=True,
)
Supported Optimizers
You can check the supported optimizers with below code.
from pytorch_optimizer import get_supported_optimizers
supported_optimizers = get_supported_optimizers()
| Optimizer | Description | Official Code | Paper | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AdaBelief | Adapting Step-sizes by the Belief in Observed Gradients | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.07468 | cite |
| AdaBound | Adaptive Gradient Methods with Dynamic Bound of Learning Rate | github | https://openreview.net/forum?id=Bkg3g2R9FX | cite |
| AdaHessian | An Adaptive Second Order Optimizer for Machine Learning | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.00719 | cite |
| AdamD | Improved bias-correction in Adam | https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.10828 | cite | |
| AdamP | Slowing Down the Slowdown for Momentum Optimizers on Scale-invariant Weights | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.08217 | cite |
| diffGrad | An Optimization Method for Convolutional Neural Networks | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1909.11015v3 | cite |
| MADGRAD | A Momentumized, Adaptive, Dual Averaged Gradient Method for Stochastic | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.11075 | cite |
| RAdam | On the Variance of the Adaptive Learning Rate and Beyond | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.03265 | cite |
| Ranger | a synergistic optimizer combining RAdam and LookAhead, and now GC in one optimizer | github | https://bit.ly/3zyspC3 | cite |
| Ranger21 | a synergistic deep learning optimizer | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.13731 | cite |
| Lamb | Large Batch Optimization for Deep Learning | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1904.00962 | cite |
| Shampoo | Preconditioned Stochastic Tensor Optimization | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.09568 | cite |
| Nero | Learning by Turning: Neural Architecture Aware Optimisation | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.07227 | cite |
| Adan | Adaptive Nesterov Momentum Algorithm for Faster Optimizing Deep Models | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.06677 | cite |
| Adai | Disentangling the Effects of Adaptive Learning Rate and Momentum | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2006.15815 | cite |
| SAM | Sharpness-Aware Minimization | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2010.01412 | cite |
| ASAM | Adaptive Sharpness-Aware Minimization | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.11600 | cite |
| GSAM | Surrogate Gap Guided Sharpness-Aware Minimization | github | https://openreview.net/pdf?id=edONMAnhLu- | cite |
| D-Adaptation | Learning-Rate-Free Learning by D-Adaptation | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.07733 | cite |
| AdaFactor | Adaptive Learning Rates with Sublinear Memory Cost | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.04235 | cite |
| Apollo | An Adaptive Parameter-wise Diagonal Quasi-Newton Method for Nonconvex Stochastic Optimization | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2009.13586 | cite |
| NovoGrad | Stochastic Gradient Methods with Layer-wise Adaptive Moments for Training of Deep Networks | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1905.11286 | cite |
| Lion | Symbolic Discovery of Optimization Algorithms | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.06675 | cite |
| Ali-G | Adaptive Learning Rates for Interpolation with Gradients | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.05661 | cite |
| SM3 | Memory-Efficient Adaptive Optimization | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1901.11150 | cite |
| AdaNorm | Adaptive Gradient Norm Correction based Optimizer for CNNs | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.06364 | cite |
| RotoGrad | Gradient Homogenization in Multitask Learning | github | https://openreview.net/pdf?id=T8wHz4rnuGL | cite |
| A2Grad | Optimal Adaptive and Accelerated Stochastic Gradient Descent | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.00553 | cite |
| AccSGD | Accelerating Stochastic Gradient Descent For Least Squares Regression | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.08227 | cite |
| SGDW | Decoupled Weight Decay Regularization | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1711.05101 | cite |
| ASGD | Adaptive Gradient Descent without Descent | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.09529 | cite |
| Yogi | Adaptive Methods for Nonconvex Optimization | NIPS 2018 | cite | |
| SWATS | Improving Generalization Performance by Switching from Adam to SGD | https://arxiv.org/abs/1712.07628 | cite | |
| Fromage | On the distance between two neural networks and the stability of learning | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2002.03432 | cite |
| MSVAG | Dissecting Adam: The Sign, Magnitude and Variance of Stochastic Gradients | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.07774 | cite |
| AdaMod | An Adaptive and Momental Bound Method for Stochastic Learning | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.12249 | cite |
| AggMo | Aggregated Momentum: Stability Through Passive Damping | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.00325 | cite |
| QHAdam | Quasi-hyperbolic momentum and Adam for deep learning | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.06801 | cite |
| PID | A PID Controller Approach for Stochastic Optimization of Deep Networks | github | CVPR 18 | cite |
| Gravity | a Kinematic Approach on Optimization in Deep Learning | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.09192 | cite |
| AdaSmooth | An Adaptive Learning Rate Method based on Effective Ratio | https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.00825v1 | cite | |
| SRMM | Stochastic regularized majorization-minimization with weakly convex and multi-convex surrogates | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2201.01652 | cite |
| AvaGrad | Domain-independent Dominance of Adaptive Methods | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.01823 | cite |
| PCGrad | Gradient Surgery for Multi-Task Learning | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2001.06782 | cite |
| AMSGrad | On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond | https://openreview.net/pdf?id=ryQu7f-RZ | cite | |
| Lookahead | k steps forward, 1 step back | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.08610 | cite |
| PNM | Manipulating Stochastic Gradient Noise to Improve Generalization | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.17182 | cite |
| GC | Gradient Centralization | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2004.01461 | cite |
| AGC | Adaptive Gradient Clipping | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2102.06171 | cite |
| Stable WD | Understanding and Scheduling Weight Decay | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2011.11152 | cite |
| Softplus T | Calibrating the Adaptive Learning Rate to Improve Convergence of ADAM | https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.00700 | cite | |
| Un-tuned w/u | On the adequacy of untuned warmup for adaptive optimization | https://arxiv.org/abs/1910.04209 | cite | |
| Norm Loss | An efficient yet effective regularization method for deep neural networks | https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.06583 | cite | |
| AdaShift | Decorrelation and Convergence of Adaptive Learning Rate Methods | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1810.00143v4 | cite |
| AdaDelta | An Adaptive Learning Rate Method | https://arxiv.org/abs/1212.5701v1 | cite | |
| Amos | An Adam-style Optimizer with Adaptive Weight Decay towards Model-Oriented Scale | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.11693 | cite |
| SignSGD | Compressed Optimisation for Non-Convex Problems | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1802.04434 | cite |
| Sophia | A Scalable Stochastic Second-order Optimizer for Language Model Pre-training | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2305.14342 | cite |
| Prodigy | An Expeditiously Adaptive Parameter-Free Learner | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.06101 | cite |
| PAdam | Closing the Generalization Gap of Adaptive Gradient Methods in Training Deep Neural Networks | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1806.06763 | cite |
| LOMO | Full Parameter Fine-tuning for Large Language Models with Limited Resources | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/2306.09782 | cite |
| Tiger | A Tight-fisted Optimizer, an optimizer that is extremely budget-conscious | github | cite | |
| CAME | Confidence-guided Adaptive Memory Efficient Optimization | github | https://aclanthology.org/2023.acl-long.243/ | cite |
Supported LR Scheduler
You can check the supported learning rate schedulers with below code.
from pytorch_optimizer import get_supported_lr_schedulers
supported_lr_schedulers = get_supported_lr_schedulers()
| LR Scheduler | Description | Official Code | Paper | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Explore-Exploit | Wide-minima Density Hypothesis and the Explore-Exploit Learning Rate Schedule | https://arxiv.org/abs/2003.03977 | cite | |
| Chebyshev | Acceleration via Fractal Learning Rate Schedules | https://arxiv.org/abs/2103.01338 | cite |
Supported Loss Function
You can check the supported loss functions with below code.
from pytorch_optimizer import get_supported_loss_functions
supported_loss_functions = get_supported_loss_functions()
| Loss Functions | Description | Official Code | Paper | Citation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Label Smoothing | Rethinking the Inception Architecture for Computer Vision | https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.00567 | cite | |
| Focal | Focal Loss for Dense Object Detection | https://arxiv.org/abs/1708.02002 | cite | |
| Focal Cosine | Data-Efficient Deep Learning Method for Image Classification Using Data Augmentation, Focal Cosine Loss, and Ensemble | https://arxiv.org/abs/2007.07805 | cite | |
| LDAM | Learning Imbalanced Datasets with Label-Distribution-Aware Margin Loss | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.07413 | cite |
| Jaccard (IOU) | IoU Loss for 2D/3D Object Detection | https://arxiv.org/abs/1908.03851 | cite | |
| Bi-Tempered | The Principle of Unchanged Optimality in Reinforcement Learning Generalization | https://arxiv.org/abs/1906.03361 | cite | |
| Tversky | Tversky loss function for image segmentation using 3D fully convolutional deep networks | https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.05721 | cite | |
| Lovasz Hinge | A tractable surrogate for the optimization of the intersection-over-union measure in neural networks | github | https://arxiv.org/abs/1705.08790 | cite |
Useful Resources
Several optimization ideas to regularize & stabilize the training. Most of the ideas are applied in Ranger21 optimizer.
Also, most of the captures are taken from Ranger21 paper.
Adaptive Gradient Clipping
This idea originally proposed in NFNet (Normalized-Free Network) paper. AGC (Adaptive Gradient Clipping) clips gradients based on the unit-wise ratio of gradient norms to parameter norms.
Gradient Centralization
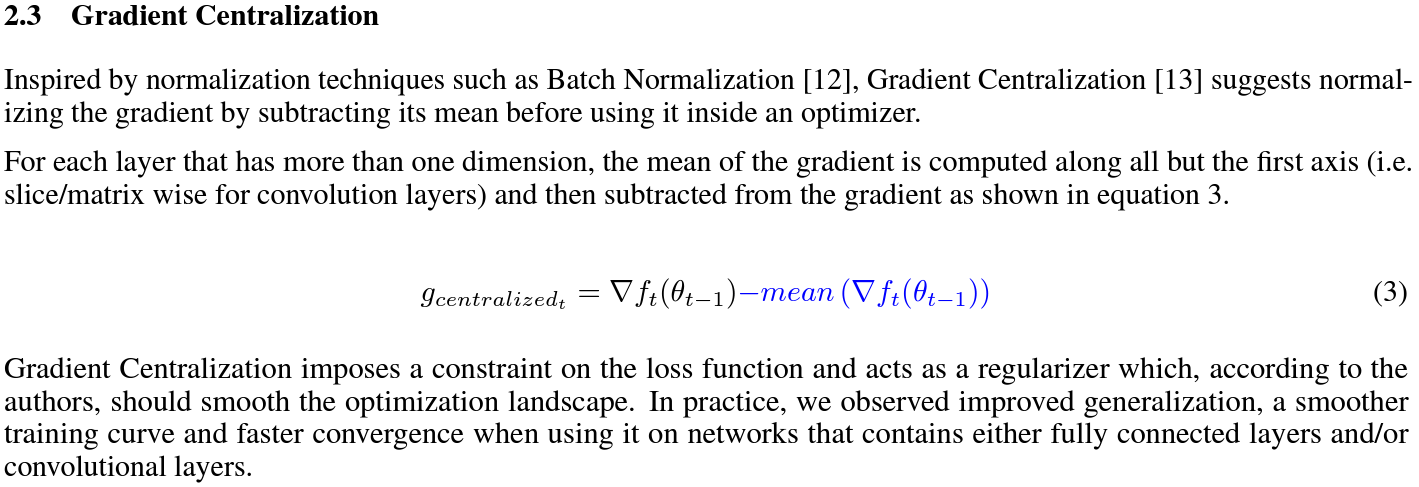 |
Gradient Centralization (GC) operates directly on gradients by centralizing the gradient to have zero mean.
Softplus Transformation
By running the final variance denom through the softplus function, it lifts extremely tiny values to keep them viable.
- paper : arXiv
Gradient Normalization
Norm Loss
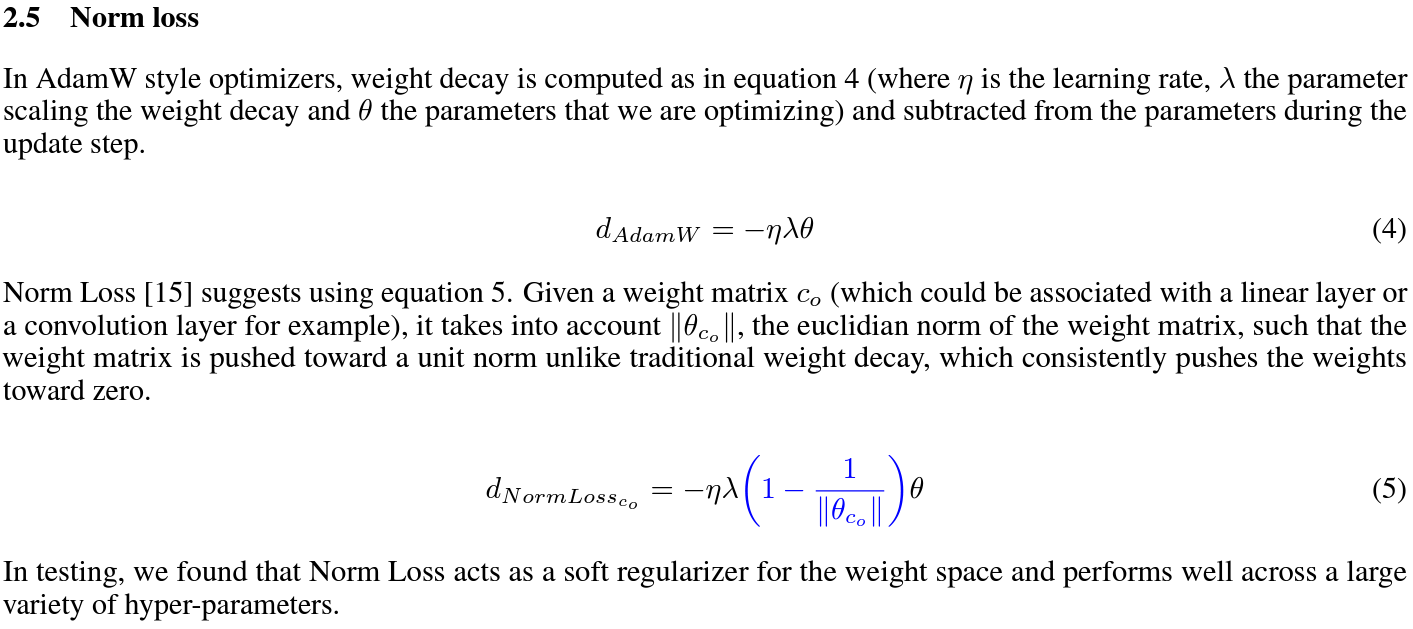 |
- paper : arXiv
Positive-Negative Momentum
 |
Linear learning rate warmup
 |
- paper : arXiv
Stable weight decay
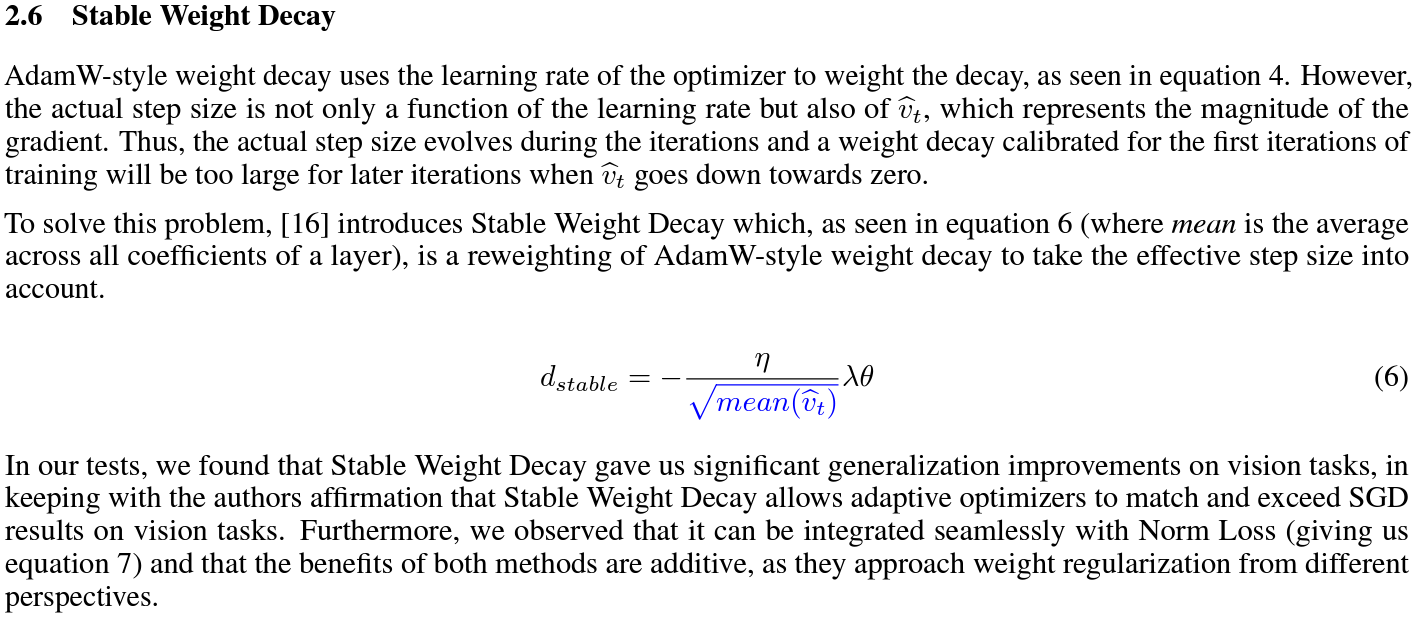 |
Explore-exploit learning rate schedule
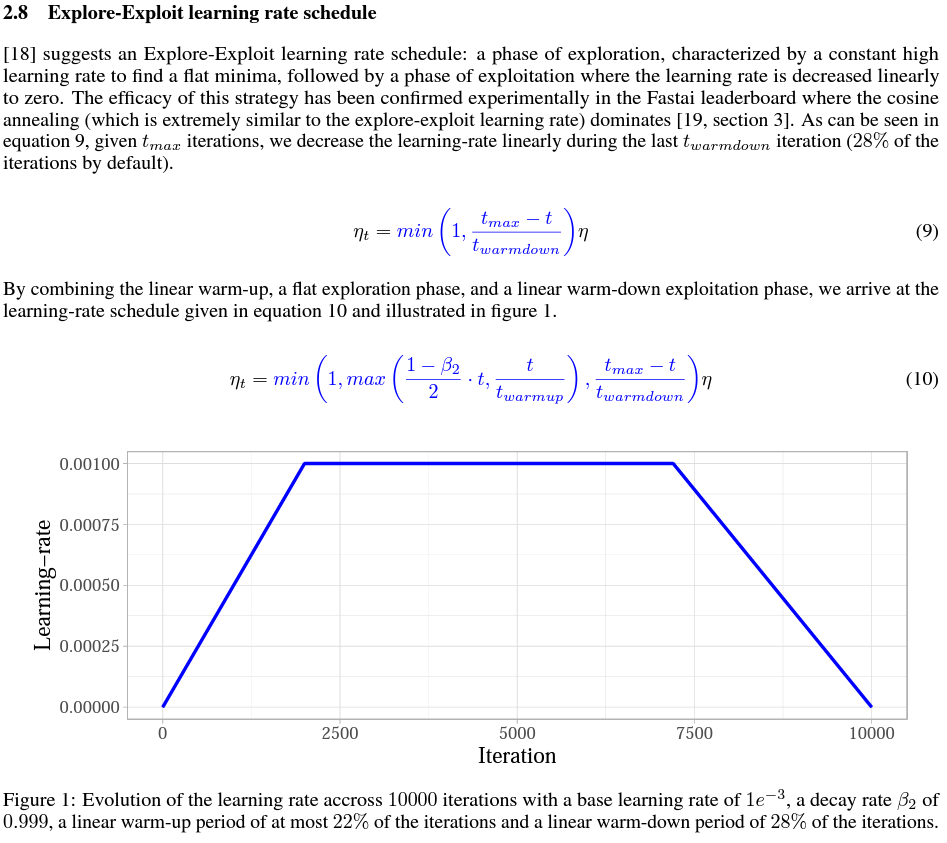 |
Lookahead
k steps forward, 1 step back. Lookahead consisting of keeping an exponential moving average of the weights that is updated and substituted to the current weights every k lookahead steps (5 by default).
Chebyshev learning rate schedule
Acceleration via Fractal Learning Rate Schedules.
(Adaptive) Sharpness-Aware Minimization
Sharpness-Aware Minimization (SAM) simultaneously minimizes loss value and loss sharpness.
In particular, it seeks parameters that lie in neighborhoods having uniformly low loss.
On the Convergence of Adam and Beyond
Convergence issues can be fixed by endowing such algorithms with 'long-term memory' of past gradients.
Improved bias-correction in Adam
With the default bias-correction, Adam may actually make larger than requested gradient updates early in training.
Adaptive Gradient Norm Correction
Correcting the norm of a gradient in each iteration based on the adaptive training history of gradient norm.
Frequently asked questions
Citation
Please cite the original authors of optimization algorithms. You can easily find it in the above table! If you use this software, please cite it below. Or you can get it from "cite this repository" button.
@software{Kim_pytorch_optimizer_optimizer_2021,
author = {Kim, Hyeongchan},
month = jan,
title = {{pytorch_optimizer: optimizer & lr scheduler & loss function collections in PyTorch}},
url = {https://github.com/kozistr/pytorch_optimizer},
version = {2.12.0},
year = {2021}
}
Maintainer
Hyeongchan Kim / @kozistr